Spark join
2024-02-27
em đã dùng các chiến lược join nào của spark
Spark join
default: sort merge join
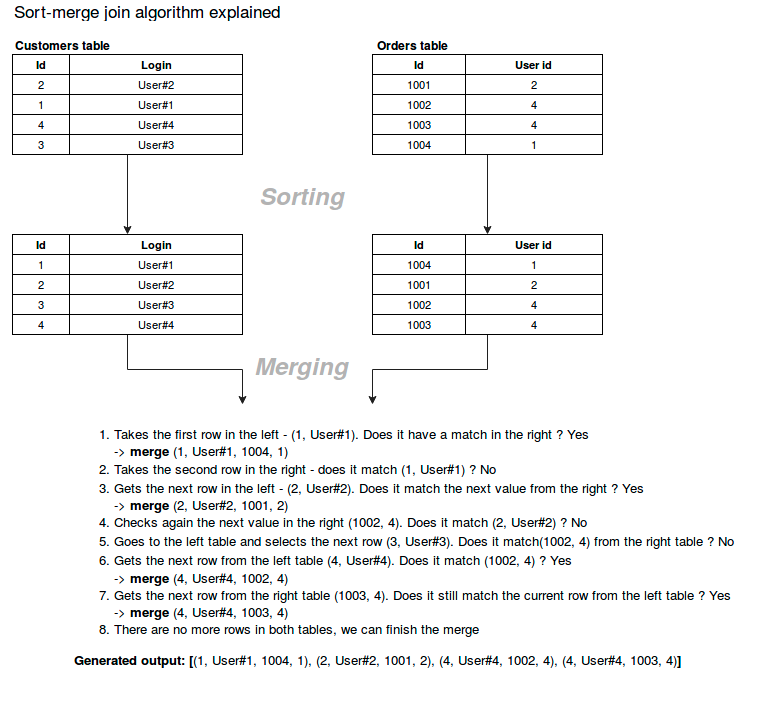
- It is necessary that the data on each partition has the same key values, so the partitions have to be co-located (in this context it is the same as co-partitioned). This is done by shuffling the data.
- Sort the data within each partition in parallel.
- Join the sorted and partitioned data. This is basically the merging of a dataset by iterating over the elements and joining the rows having the same value for the join key.
Shuffle when join can be avoided if:
- Both dataframes have a common Partitioner.
- One of the dataframes is small enough to fit into the memory, in which case we can use a broadcast hash join.
Same partitioner example
users = users.repartition('userId').cache() # do not forget to cache!
joined1 = users.join(addresses, 'userId')
joined1.show() # 1st shuffle for repartition
joined2 = users.join(salary, 'userId')
joined2.show() # skips shuffle for users since it's already been repartitioned
Ngoài ra: Broadcast Hash Join (khi một bên join có kích thước nhỏ - broadcast ra hết), Shuffle Hash Join, Broadcast Nested Loop Join
spark.conf.set("spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold", byte or -1 disable )
| Chiến lược Join | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| Broadcast Hash Join | df1.join(broadcast(df2), "key") Sử dụng broadcast để phát tán bảng nhỏ. |
| Shuffle Hash Join | Khi 2 table đều lớn. cần phải set preferSortMergeJoin = false thì mới chạy chiến lược này vì ưu tiên sort merge join hơn |
| Sort Merge Join default | Sắp xếp hai bảng trước khi thực hiện join |
| Broadcast Nested Loop Join | Sử dụng 2 vòng for |
